[
] 116
A B
et ter
W
or ld
related problems. The programme has generated specific
guidelines and educational initiatives for the local commu-
nity in the understanding of flood risk management plans.
The programme was led by Dr. Foo Keng Yuen from the
River Engineering and Urban Drainage Research Centre and
Dr. Lee Lai Kuan from the School of Industrial Technology,
along with their research group. Free health screening and
consultation related to the nutritional and health status of
flood-affected populations were provided by a group of well-
trained facilitators. Well-structured questionnaire surveys
were conducted in the areas vulnerable to flood to compile
data on socio-demographic background, past flood experi-
ence, drinking water sources, food aid systems, sanitation
and hygiene, as well as the health risks of the affected popu-
lation during exposure to flood events.
The survey was supported by over 1,500 participants from
flood-prone areas in Perlis, Kedah, Perak, Pulau Pinang,
Selangor, Melacca, Kelantan, Pahang, Terengganu and Johor.
In conjunction with the awareness programme, several
technical and non-technical talks related to issues of water
safety, hygiene, sanitation levels, and flood borne diseases
were delivered by professional health experts for knowledge
enhancement, environmental preservation, and upgrading
social welfare and quality of life among the flood victims.
Alongside the programme, coping strategies, the appli-
cation of appropriate sanitation technology in coastal and
flood-prone areas, and effective flood risk management
approaches were proposed and introduced to safeguard the
available water resources. According to the flood-affected
populations, the shortage of clean water resources was the
most alarming challenge, as the flow of flood water was able
to damage the available water supply systems, and conven-
tional tube wells. During this period, the overflowing flood
water was mixed with clean fresh water, and the yellowish,
smelly polluted water was forced to the only supply for their
daily activities. The inefficiency of the water supply and sani-
tary facilities significantly compromised the hygiene levels
of the local community during this disaster, contributing
to the spreading of water-borne diseases, specifically among
children, women and elderly groups. The survey found that
more than 73% of the population had been suffering from
fever, dermatological symptoms and diarrhoea. An inconsist-
ent supply of food aid has further affected the nutrition and
health of the flood victims.
This collected information was shared with local authori-
ties, water regulatory bodies, health care centres, insurance
companies, and government and non-government organisa-
tions for future disaster management preparedness, with
a view to promote a resilient and sustainable society. The
accomplishment of this community-driven project has estab-
lished a water safety quality assurance strategy and integrated
flood risk management plan to generate a reliable database
and to review the available flood remedial policies, set up
effective emergency response procedures, ensure the relia-
ble management of clean potable water and water treatment
infrastructures, provide better health-care facilities, reduce
morbidity and mortality rates of vulnerable populations, and
minimise the transmission of water-borne diseases.
In conclusion, the programme has highlighted the pressing
need to underpin the joint ventures between the stake-
holders, not limited to inter-agency collaboration, public
engagement and systematic emergency plans, all of which
are indispensable for building a sustainable future.
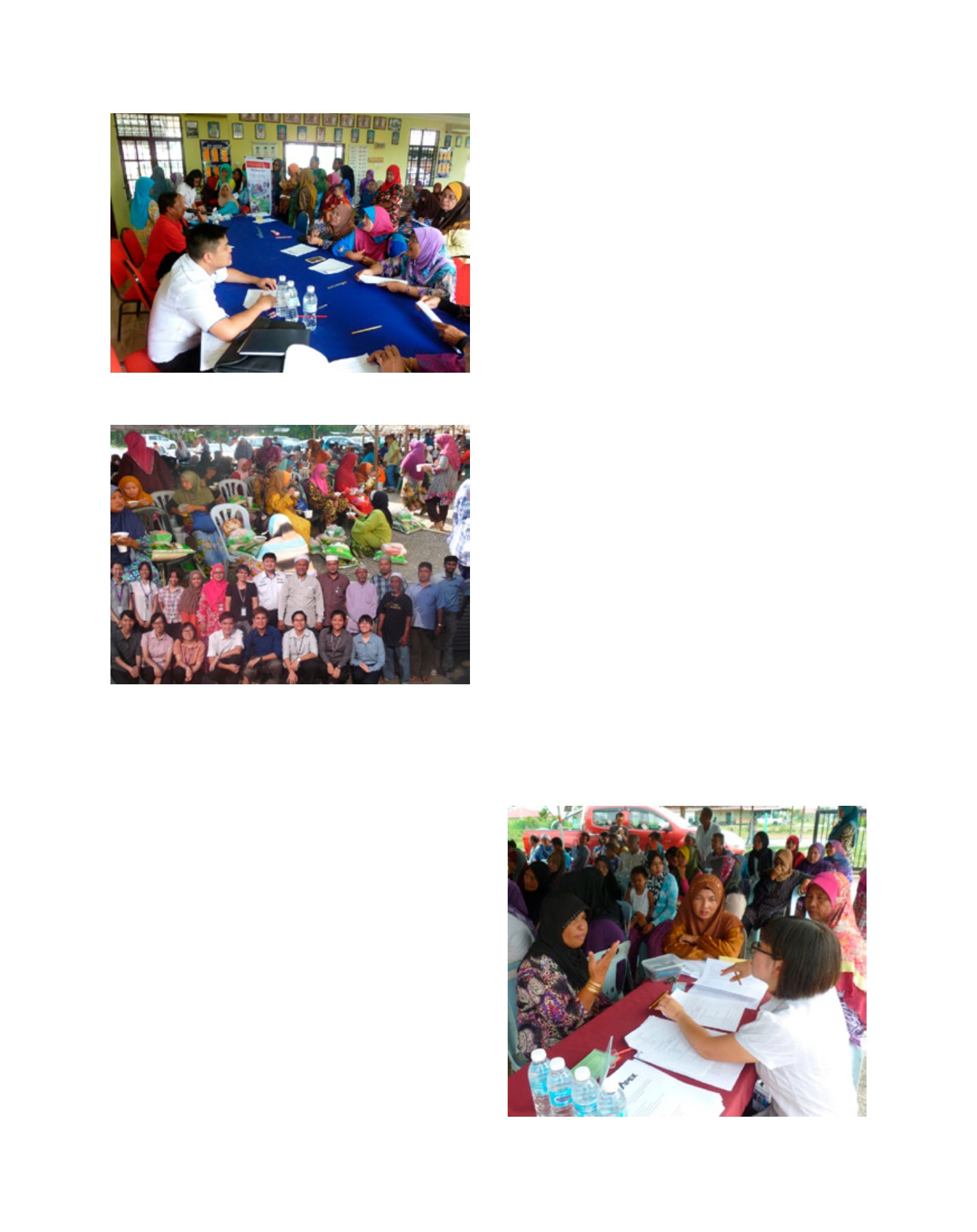
Health screening and consultation related to nutrition at a community hall
in Kampung Balok, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia
The National Flood Management Programme in Segamat, Johor, Malaysia
Questionnaire survey in Hulu Terengganu, Malaysia
Image: USM
Image: USM
Image: USM