[
] 36
access
to
water
and
sanitation
for
all
tural drought, when the surface water from storage ponds or
rivers is insufficient to complement rainwater to meet crop
water requirements, shallow tube well irrigation is a suitable
choice. However, shallow underground water, especially in
the eastern region of the Malaysian peninsular, contains high
levels of iron and is unsuitable, particularly for leafy vegeta-
bles. This problem has been overcome with the integration
of sawdust cartridge filtration into the irrigation system.
Sawdust has been found to be able to absorb up to 95% of
iron content from underground water. With a construction
cost of no more than RM2,000, this system is economical yet
highly efficient and easily operated by farmers.
Scheduling the planting
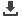
To fully exploit rainwater and achieve yield potential for
short term crops, planting dates should be timed to coincide
with the rainfall pattern. The optimum time to start sowing
is at the onset of the rainy season, with harvesting sched-
uled for the dry period. Figure 5 shows the planting schedule
based on the long term average monthly rainfall pattern for
rice cultivation in the northern state of the Malaysian penin-
sular. The planting schedule can change over time as a result
of climate change as well as changes in technological and
socio-economic factors. Thus, it is necessary to regularly
update the average rainfall and climatic data for each specific
agro-climatic zone planting schedule in order to reduce the
impact of climate change.
Land levelling
Particularly important for paddy fields, a well levelled surface
will increase the efficiency of water use, improve crop estab-
lishment, reduce input, improve machine efficiency and
reduce the need for a more intensive on-farm irrigation
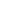
and drainage system. The availability of laser controlled
land levelling equipment (see figure 6) and ICT technology
has marked one of the most significant recent advances in
surface irrigation technology. Now, the cut and fill opera-
tions in land levelling are guided by a receiver attached to
the motor grader, based on a treatment map using the GPS
system. The improvement of land levelling technologies has
reduced standing water in rice fields from 10–15 cm to 5–10
cm. This has improved field water use significantly by reduc-
ing seepage and deep percolation.
ICT water management
ICT is making significant impact on agriculture and agri-
cultural water management. Farmers now have access
to a wealth of online information on crop prices, weather
forecasts for irrigation and water management, and plant
diseases, to influence planting decisions.
Together with GIS technology, new ways of supporting
water management are available. The telemetric system inte-
grated with GIS enables irrigators to operate water gates
and pumping systems, monitor dam water levels and supply
canals from a remote office (see figure 7). This helps the
operator to supply the right amount of water to the right
place at the right time, improving conveyance efficiency and
significantly reducing water wastage. The technology also
acts as an effective early flood warning system.
Fig 5: Rice planting schedule based on long-term
average rainfall pattern
Fig. 6: Laser-guided land levelling technology has improved surface irrigation,
particularly in rice basin areas
Fig. 7: The use of a telemetric system in the Muda Agriculture Development
Authority area to control and monitor irrigation water supply from reservoirs
to rice fields
Source: Malaysian government
Source: Malaysian government
THAILAND
MALAYSIA
SELAT MELAKA
Alor Setar
Kangar
Average monthly rainfall
Average annual rainfall 2400mm
Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec
Drought
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
Rainfall (mm)
Off-season crop
Main-season crop
Image: MARDI
Rainfall station
Rainfall and evaporation station
Rainfall and water level station
Rainfall, water level and telemetric station
Water level station
Water level and telemetric station