[
] 63
A B
et ter
W
or ld
for all citizens. To tackle rising demand, the strategy focuses
on generating additional water resources and encouraging
responsible consumption. Under this vision, the plan is to
build 59 dams, construct desalination plants, and increase the
reuse of treated wastewater and the collection of rainwater.
The government will also introduce water-saving technolo-
gies, particularly in irrigation, improve efficiency in its water
networks, revise water tariffs, and encourage water recycling.
3
Boosting water supply to households and to
the agricultural sector
Agriculture production is a major driving force of Morocco’s
economy, making up 19% of its GDP (agriculture 15%, agro-
industry 4%), and employing 4 million or 40% of the labour
force.
4
However, the agriculture sector is highly dependent
on rainfall with only 15% of its total agricultural land being
irrigated, making it extremely vulnerable in times of low
rainfall and drought.
5
To reform the agricultural sector and
integrate agricultural production into international markets,
a national agricultural strategy – the Green Morocco Plan –
was adopted in 2008. The Plan is designed to promote the
development of a sustainable, modern, and competitive agri-
culture sector. To reduce risks and volatility in the sector, the
Government has focused on investments in irrigation and the
improvement of water management.
6
Several initiatives have
been introduced under the Plan, which is also integrated
into the National Water Strategy, such as the construction
of dams, connecting the dams with irrigation schemes to
improve water supply, the introduction of water-saving irri-
gation techniques, and the conservation of groundwater.
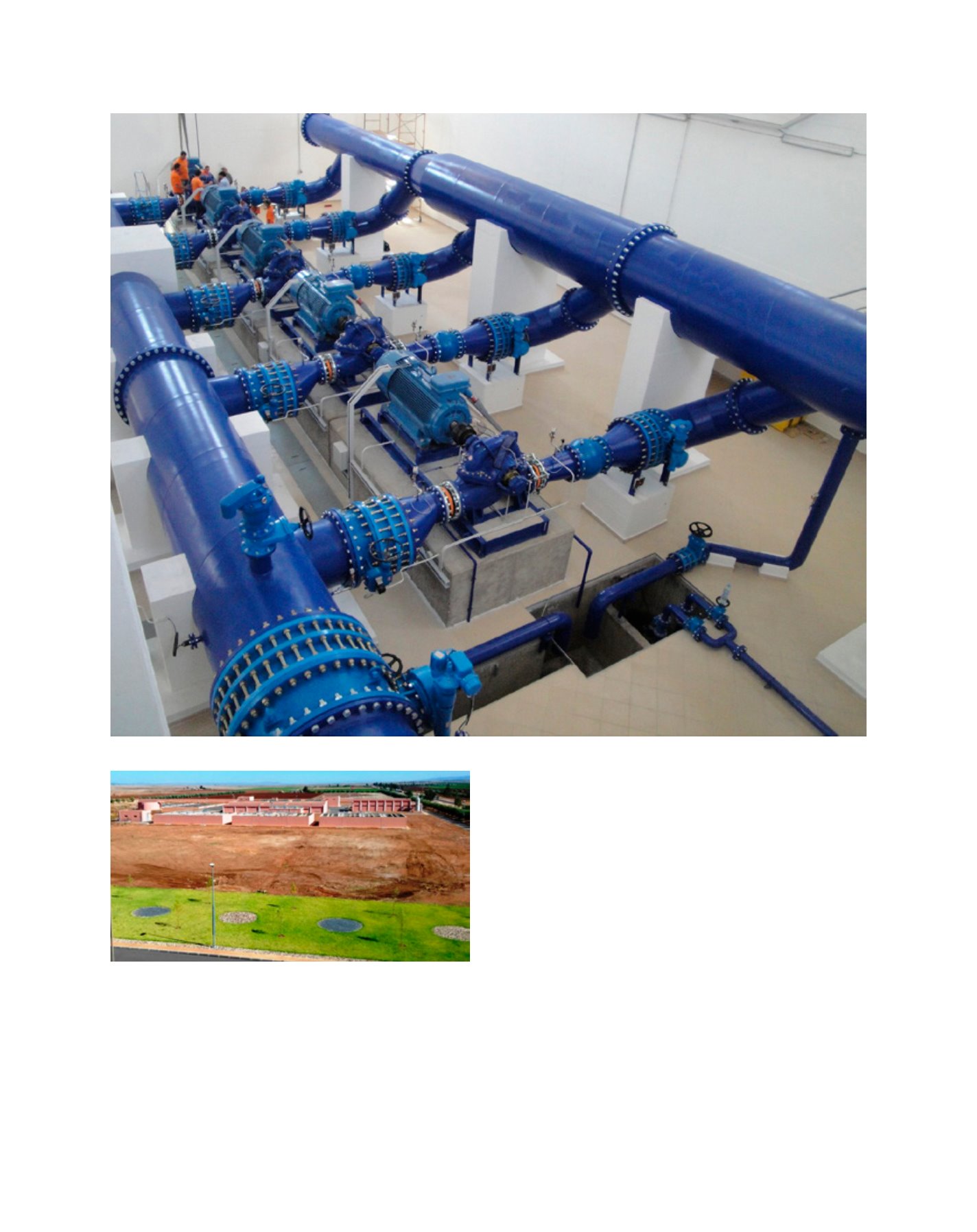
Pumping station
General view of the wastewater treatment plant
Image: MoFAIC UAE
Image: MoFAIC UAE